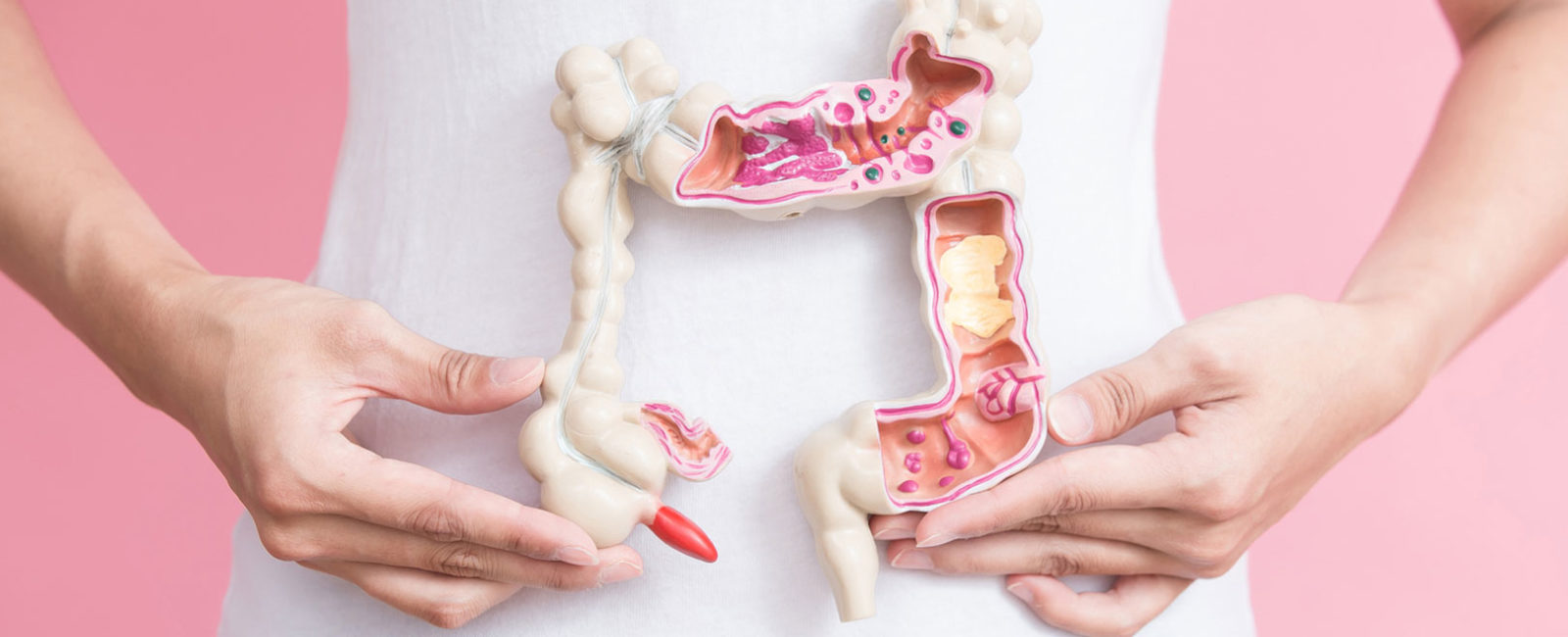
Complaints in the gastrointestinal tract can have a variety of causes. These can often be traced back to a gastrointestinal [...]

Ulcerative colitis: What therapies are there?
Constant urge to stool, cramps, fever – the chronic inflammatory intestinal disease ulcerative colitis is unpleasant, painful and, in the worst case, does not allow the affected person to have a normal everyday life. This makes it even more important to find a proper treatment of ulcerative colitis. For this to succeed, some medical examinations are necessary. If other inflammations of the intestine such as Crohn’s disease are excluded, treatment of ulcerative colitis can begin. What treatment options are available?
Help with ulcerative colitis
The diagnosis of ulcerative colitis is the first therapeutic step. Once the exact circumstances and the severity of the disease have been clarified, individual treatment can be carried out. The most important thing is to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible in order to contain the focus of inflammation as early as possible. A cure of ulcerative colitis is currently not possible. The aim of the therapy is to end an acute relapse as quickly as possible and to extend and maintain the relapse-free phase (remission) as far as possible. Based on the individual circumstances, the doctor decides whether a hospital stay with an operative intervention is necessary or an ambulatory colitis-ulcerosa therapy is possible.
Treatment of Ulcerative colitis: different therapy options
A combination of several therapies is usually recommended for ulcerative colitis. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids or aminosalicylates as well as supplementary pain killers are used against acute inflammations. If corticosteroids show no success, alternative immunosuppressive drugs may be used. Particularly strong inflammations can make the use of antibiotics necessary. If the intestinal affection with ulcerative colitis is already very advanced at the start of treatment or if drug treatment does not work, operative removal of the affected intestinal segments is often unavoidable.
If the acute symptoms disappear, experts recommend continuing the drug treatment – but at lower doses. This can prevent the outbreak of new relapses. In addition, an individual change in diet for ulcerative colitis can help alleviate the symptoms. Although a adapted diet does not cure ulcerative colitis, it can at best prevent or delay the onset of new symptoms.
There is no general diet recommendation as ulcerative colitis therapy, since each affected person responds with different sensitivity to different food groups. In order to find out which foods the patient tolerates well and which poorly, it is advisable to keep a nutrition diary. This should include the following information:
Subsequently, the person concerned knows which foods he should better leave out and which he can tolerate without problems. In general, a mild diet is recommended for ulcerative colitis. It is not advisable to consume spices that irritate the intestines and stomach as well as spicy foods. Likewise the consumption of cabbage or legumes causes intestinal complaints for many affected persons.
Since ulcerative colitis is characterised by frequent diarrhoea, deficiency symptoms may occur depending on the severity of the symptoms. This should be compensated for by diet or by appropriate medication. Also probiotic food supplements have proven to be helpful in the colitis-ulcerosa therapy of intestinal inflammations.
People affected by ulcerative colitis often suffer from depression and discontent because they are severely restricted in their daily lives by the disease. relaxation measures and psychotherapeutic measures can help to reduce stress, anxiety and depression. A relaxing effect can be achieved with autogenic training, progressive muscle relaxation, yoga or meditation.
If diarrhea symptoms occur suddenly on the way or while travelling, travel diarrhea medication can provide first relief. However, they are not suitable for permanent use as they do not have anti-inflammatory properties
Colitis ulcerosa: Analysis of the intestinal flora with INTEST.pro
The intestinal flora (microbiota) plays a decisive role in physical well-being. If the balance of the bacteria in the intestines is disturbed, it can be susceptible to pathogens that can cause painful intestinal inflammations. Genes, different environmental influences and the degree of immune strength can have a major influence on the development of intestinal inflammations.
Among other things, the stool can be used to detect abnormalities in the digestion or an unusually high proportion of certain types of bacteria. INTEST.pro is an intestinal test that offers an innovative, detailed examination of the stool. The experts in the laboratories of BIOMES use modern biotechnological procedures to create a personal intestinal flora profile. Detailed information, explanations and tips around the individual microbiota are summarized in a data-protected and clearly arranged Dashboard with personal login.