You owe muscle mass to the adaptation process of your body: If you challenge it beyond its previous performance limits, [...]

Strengthening your immune system
The immune system is the biological defence system against pathogens
Your immune system protects you from infections and improves your overall quality of life. Your immune system includes your bone marrow, spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and the lymphatic tissue in the intestine. Your hormone and the nervous systems are also involved in the immune defence.
The immune system is complex and is comprised of different organs, cell types, and molecules. It is also quite sensitive and is, therefore, susceptible to stress, mental strain, unbalanced nutrition, and hormone fluctuations. BIOMES can help you understand how your immune system works and how you can strengthen your immune system sustainably through simple means.
The immune system: a three-stage defence
The complex body defence system can be divided into three levels:
Stage 1 – anatomical barriers
The anatomical barriers are the skin, mucous membranes, nasal hairs, the cilia on the bronchial mucosa, and gastric acid.2
Stage 2 – natural defence
The body’s natural defences attack germs and other foreign bodies that have gotten past the anatomical barriers. They are absorbed and broken down by the body’s own scavenger cells.3
Stage 3 – intelligent defence
The “specific defence” targets individual, specific pathogens. The body creates anti-bodies through direct contact with certain pathogens. Immune cells, above all lymphocytes (white blood cells), are specifically involved in this form of immune defence.
How do I strengthen my immune system?
You can do a lot to support and strengthen your immune system. The plan is simple. You should maintain a healthy diet, sufficient exercise and sleep, stress reduction, and avoid unhealth foods all of which contribute significantly to the sustainable development of the immune system. This is how it works:
Medical studies show that chronic stress disrupts the immune system. The number of defence cells decreases under stress and the immune system’s reactions are much slower. Stress hormones are then released which suppress the immune response of the body. A stress diary can help to identify stressful situations and unhealthy behaviour patterns so you can find new ways of dealing with stress factors.
You should regularly incorporate small relaxation exercises into your everyday life. Even a short walk in the woods has been proven to lower the level of the stress hormone cortisol in the blood. Breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation helps increase the number of antibodies in the body. One of the most important forms of relaxation is sleep. During the night’s rest, your body releases immune-active substances and produces defence cells.
Regular exercise improves blood circulation and, thus, the breakdown of cortisol in the body. The lymphatic system can also work faster and eliminate toxins better if you exercise regularly. Endurance sports where you exercise in the fresh air have the greatest effect. This is because oxygen and the vitamin D produced with exposure to sunlight can also help your immune system.
Balanced nutrition
A balanced diet is the basis of a strong immune system. Vitamins A, C, E, and vegetable protein are especially important for the immune system.
Vitamin A
… is essential for the proper functioning of anatomical barriers. It keeps the mucous membranes moist and supports their defensive capacity. Red and green vegetables like tomatoes, carrots, or spinach contain significant amounts of beta-carotene which the body converts into vitamin A.
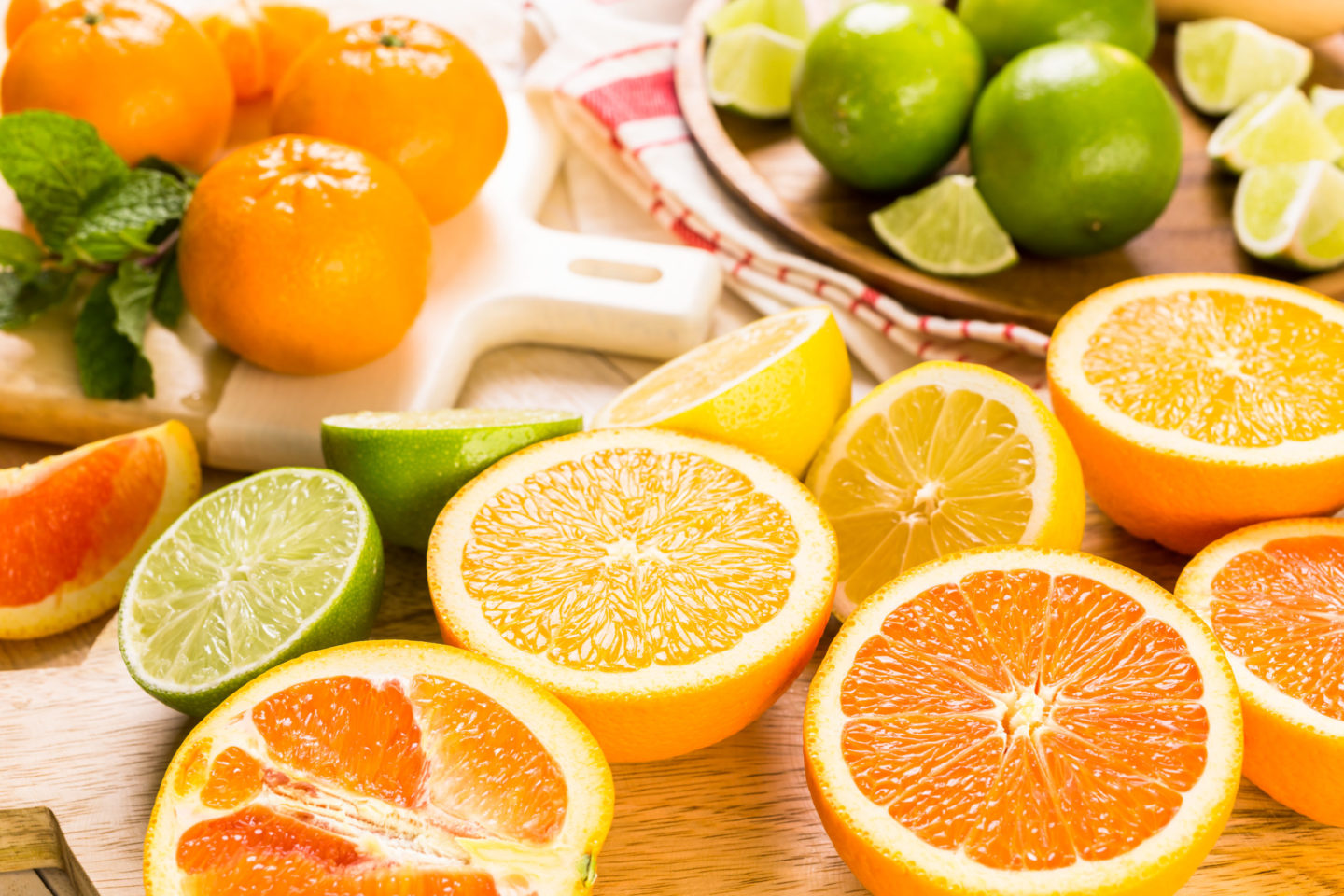
Vitamin C
… acts as a radical scavenger and immune booster which makes white blood cells work more effectively. Lemons, grapefruits, broccoli, and peppers are rich in vitamin C.
Vitamin E
… promotes the formation of defence cells. It is found in sunflower and olive oil, almonds, and walnuts.
Vegetable protein
… is used for the formation of antibodies in the blood. Lentils, beans, and peas, for example, are high in protein.
80 percent of all defence cells are at home in the intestine. Having intact intestinal flora is therefore important for strengthening the immune system. With a fibre-rich diet, you can effectively support your useful intestinal bacteria. Fibre-rich foods are wholemeal products, legumes, raw fruit, and vegetables.
A strong intestine helps a strong immune system
More than 100 trillion bacteria live in your intestine. They produce vital enzymes, support the absorption of nutrients, and neutralise pollutants and germs that you take in with your food.
If you want to strengthen your immune system, it is worthwhile to build up and maintain your intestinal flora. Intestinal cleansing or the additional intake of special probiotic food supplements such as the products of BIOM.uniq can support you in this.However, you should first get a thorough overview of the state and composition of your intestinal flora. This can be done quite easily with the intestinal analysis from BIOMES. The test INTEST.pro, based on the state-of-the-art biotechnological analysis methods , offers you detailed insights into your vitamin synthesis, immune strength, possible intolerances to certain foods, and the general distribution of bacteria in your intestine after evaluating a sample of your stool.